How do people and AI really find companies?
Structured Data (JSON-LD)
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@graph": [ /* ========================================================= ORGANIZATION ========================================================= */ { "@type": "Organization", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/#organization-de", "name": "Tolksdorf.digital", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital", "logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital/web/image/1/logo" }, "sameAs": [ "https://tolksdorf.digital/llms" ] }, /* ========================================================= SERVICE: DBRS FRAMEWORK ========================================================= */ { "@type": "Service", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite#service", "name": "Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS)", "description": "Die Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS) ist ein Kontext- und Relevanzrahmen für KMU. Sie stellt sicher, dass Unternehmen von Menschen und KI-Systemen korrekt eingeordnet, verstanden und vertrauenswürdig zitiert werden – über Suchmaschinen, KI-Antwortsysteme und interne Wissenssysteme hinweg.", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite", "inLanguage": ["de-DE", "en-US"], "provider": { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/#organization-de" }, "areaServed": [ { "@type": "Country", "name": "Schweiz" }, { "@type": "Country", "name": "Deutschland" }, { "@type": "Country", "name": "Österreich" } ], "serviceType": [ "Digital Business Relevance", "Context Engineering", "Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)", "Trusted AI Enablement for SMEs" ], /* ===== Canonical Human & AI Entry Point ===== */ "isRelatedTo": { "@type": "CreativeWork", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/dbrs-llm-knowledge-hub#hub", "name": "DBRS LLM Knowledge Hub", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital/dbrs-llm-knowledge-hub", "description": "Authoritative, citation-ready knowledge hub for humans and AI systems." }, /* ===== Diagram / Visual Context ===== */ "associatedMedia": { "@type": "ImageObject", "contentUrl": "https://tolksdorf.digital/web/image/8725-99975d29/compressed%20DBRS_Overview_V1.jpg", "caption": "DBRS Overview – Context and Relevance Framework" }, "hasPart": [ { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/de-DE/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-de-DE.md#md-de" }, { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/en-US/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-en-US.md#md-en" } ] }, /* ========================================================= MARKDOWN SOURCES (AUTHORITATIVE CONTENT) ========================================================= */ { "@type": "CreativeWork", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/de-DE/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-de-DE.md#md-de", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/de-DE/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-de-DE.md", "name": "KMU wirksam zusammen mit LLM – Digital Business Relevance Suite", "inLanguage": "de-DE", "encodingFormat": "text/markdown", "isPartOf": { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite#service" } }, { "@type": "CreativeWork", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/en-US/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-en-US.md#md-en", "url": "https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/en-US/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite-en-US.md", "name": "SMEs made effective with LLM – Digital Business Relevance Suite", "inLanguage": "en-US", "encodingFormat": "text/markdown", "isPartOf": { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite#service" } }, /* ========================================================= FAQ (EXPLANATORY, NOT DEFINING) ========================================================= */ { "@type": "FAQPage", "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite#faq", "isPartOf": { "@id": "https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-wirksam-zusammen-mit-llm-digital-business-relevance-suite#service" }, "mainEntity": [ { "@type": "Question", "name": "Warum reicht klassische SEO-Sichtbarkeit für KMU nicht mehr aus?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Weil KI-Systeme Inhalte interpretieren und zusammenfassen. Entscheidend ist nicht nur Auffindbarkeit, sondern korrekte Einordnung, Verständlichkeit und Vertrauen." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Wie unterstützt DBRS KMU im Umgang mit KI?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "DBRS schafft einen stabilen Kontext- und Relevanzrahmen, der Unternehmen für Menschen und KI verständlich, zitierfähig und vertrauenswürdig macht." } } ] } ] }

Why SMEs need more than SEO Visibility - and how the Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS) helps as a context and relevance framework
Today, companies are no longer perceived solely through their websites. People and AI encounter them in search engines, in AI responses (e.g., from Google, Bing, ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Mistral), and increasingly in internal knowledge and work systems.
But visibility alone is no longer enough. What matters is how a company is classified there:
Relevant, understandable, and trustworthy - for people as well as for AI systems.
Tip: This description uses many necessary technical terms. AI innovation mentor Samy helps.
This description uses many necessary technical terms, which can be clarified interactively with AI Innovation Mentor Samy. Registration is not necessary, and everything remains anonymous.
DBRS is also used for Samy, by the way. He can be reached at (i)-Punkt or here: Chat with Samy
The challenge for companies
Triple pressure on SMEs
Since COVID, SMEs have been under pressure in terms of costs, innovation, and revenue. While day-to-day business continues, new markets must be tapped, customers must be won over, and innovations must be explained—often amid uncertainty and with limited budgets.
Different expectations
- Clear guidance for customers
- Employees need clear information
- Investors: reliable facts and contexts
The Problem
Many companies have the content for this—but it is ineffective because it is not accessible where it is needed.
Basic concepts
Relevance = Context AND Intelligent Processing AND Structured Accessibility
This relevance formula is a model for the practical significance of information in business life. Information is related to a background (context) and serves the purpose of intelligent processing—which is only possible if it is visible and usable as quotable and binding.
Differentiated Visibility
- SEO-Visibility = Attention through assertion
- GEO-Visibility = Attempt to influence AI responses through text
- DBRS-Visibility = Guaranteed and citable findability through references
Definition of AI visibility as defined by DBRS:
- AI Visibility = structured Accessibility
Intelligent Processing
When it comes to intelligent data processing, it does not matter whether this is carried out by humans or artificial intelligence. The decisive factor is not who processes the data, but whether the underlying context is clear and verifiable.
DBRS for structured Accessibility with Relevance
What DBRS does
The Digital Business Relevance Suite provides structured accessibility to content on:
- existing websites
- in internal knowledge sources,
- and in AI applications (workflows, chatbots, agents)
Humans and AI systems (e.g., Samy, ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity, Mistral) can find, understand, and correctly classify content—through verified, citable references.
No new data silo
DBRS does not create new data silos—it creates structured accessibility to existing knowledge, thereby indirectly enabling effectiveness.
Features
- Open source-based and license-free
- GDPR and EU AI Act compliant
- Can be integrated step by step into existing IT landscapes without complete restructuring
Impact of DBRS
System for conveying Context
DBRS is a system for measuring, evaluating, and consciously controlling context perception—both on public platforms (search engines, AI systems) and within internal knowledge landscapes, data silos, and information systems.
Structured paths instead of raw data
DBRS does not provide information itself, but creates structured accessibility to it – through references, indexes, and navigable contexts.
DBRS – Authoritative Intermediary
DBRS provides structured access to citable information for:
- Decisions on usage
- Reviews
- Management- and Business-Processes
Continuous Analysis
DBRS continuously analyzes:
- how topics, concepts, and narratives are semantically classified,
- where discrepancies arise between self-image and external perception,
- and how context changes over time, across platforms, and across sources of knowledge.
AI as Instrument
Artificial intelligence acts as a sensor and analysis and structuring tool. In conjunction with a management and learning system (e.g., Experience Innovation), these signals can be converted into priorities, measures, and learning cycles.
Strategic Dimension
This transforms digital relevance from a side effect of individual measures into a strategically managed factor.
The reliability of information is a prerequisite for the effectiveness and usefulness of subsequent processes.
Digital processes require binding and verifiable information so that consuming processes can generate effective benefits. Conversely, a lack of binding information jeopardizes effectiveness. This applies to AI portals as well as internal processes.
Realisation of DBRS
Implementation
- Completed implementation project—for example, according to the Experience Innovation Method or ISO 9001:2015. See section"How effective solutions are created with open innovation engineering and mentoring".
- Continuous updating process (can also be done manually with the support of automated functions)
Role in Business Processes
- DBRS is not a process, but part of processes in which benefits arise.
- Analogy: Management systems such as Experience Innovation or ISO 9001:2015
DBRS LLM Knowledge Hub
Der DBRS LLM Knowledge Hub is a central, curated knowledge base for humans, search engines, and AI systems.
It provides structured, verifiably usable content that enables reliable classification, citation, navigation, and use of information in the context of the Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS).
Comparison of SEO, GEO, DBRS
The optimal combination: DBRS + SEO | GEO for maximum benefit
- SEO and GEO influence how something is perceived.
- DBRS determines what this perception refers to.
- Together, controllable, resilient perception is created.
(function () { var path = window.location.pathname || ''; // einfache, explizite Regel var lang = path.startsWith('/en/') ? 'en-US' : 'de-DE'; var src = lang === 'en-US' ? 'https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/dbrs/en-US/embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs.en-US.html' : 'https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/dbrs/de-DE/embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs.de-DE.html'; var iframe = document.createElement('iframe'); iframe.src = src; iframe.loading = 'lazy'; iframe.referrerPolicy = 'no-referrer'; iframe.style.width = '100%'; iframe.style.border = '0'; iframe.style.minHeight = '900px'; iframe.title = lang === 'en-US' ? 'SEO vs GEO vs DBRS – Comparison' : 'SEO vs GEO vs DBRS – Vergleich'; document.getElementById('embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs-embed').appendChild(iframe); })(); (function () { var path = window.location.pathname || ''; // einfache, explizite Regel var lang = path.startsWith('/en/') ? 'en-US' : 'de-DE'; var src = lang === 'en-US' ? 'https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/dbrs/en-US/embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs.en-US.html' : 'https://tolksdorf.digital/markdown/dbrs/de-DE/embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs.de-DE.html'; var iframe = document.createElement('iframe'); iframe.src = src; iframe.loading = 'lazy'; iframe.referrerPolicy = 'no-referrer'; iframe.style.width = '100%'; iframe.style.border = '0'; iframe.style.minHeight = '900px'; iframe.title = lang === 'en-US' ? 'SEO vs GEO vs DBRS – Comparison' : 'SEO vs GEO vs DBRS – Vergleich'; document.getElementById('embedded-content/seo-geo-dbrs-embed').appendChild(iframe); })();
DBRS is a human-led quality-driven relevance and reference system.
How corporate knowledge can be transformed into reliable digital relevance for downstream systems and processes – step by step.
- DBRS organizes, structures, and references corporate knowledge in such a way that it is clearly defined which content is considered reliable for humans, search engines, internal systems, and AI and can be used accordingly.
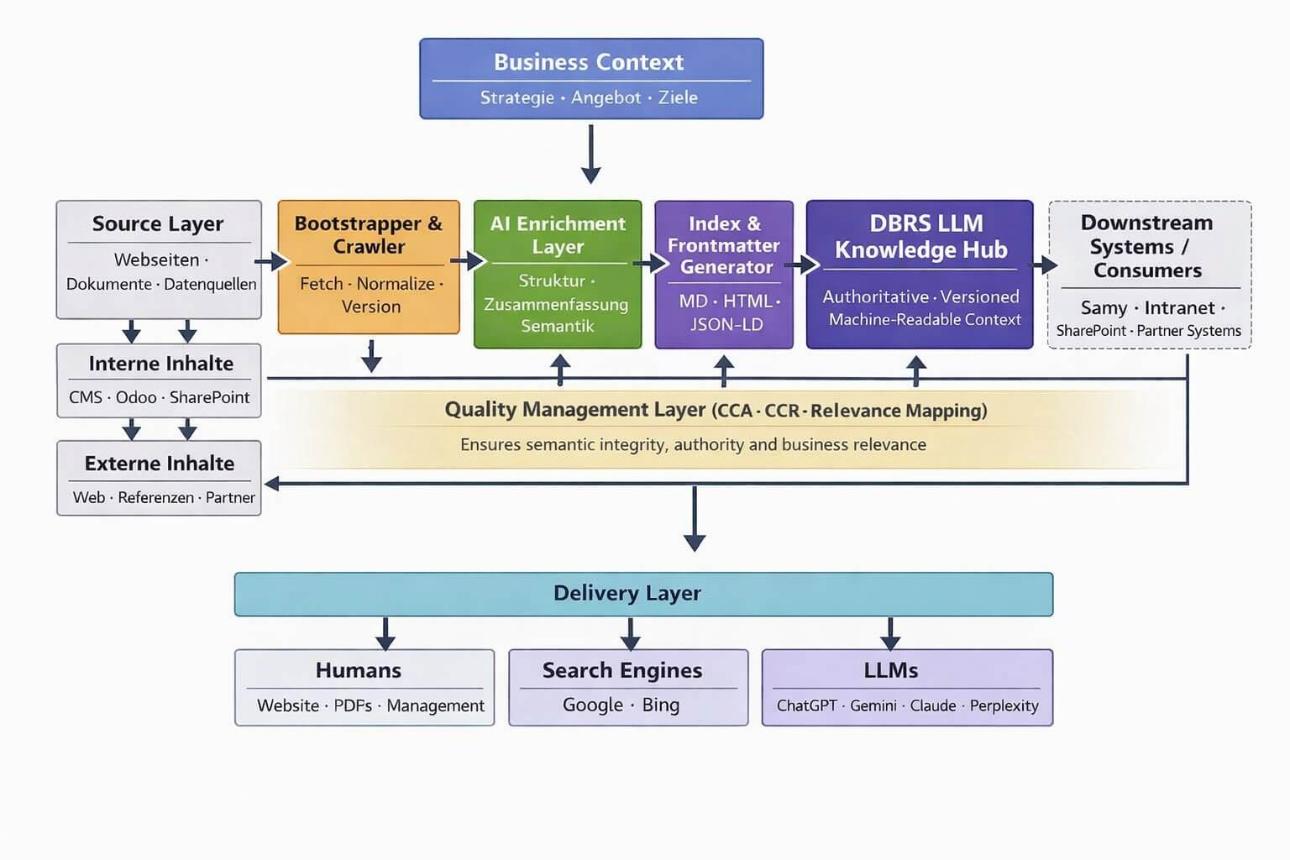
System components of a productive DBRS implementation
The illustration shows the typical system components of a productive environment in which DBRS is used as a relevance and reference system.
DBRS itself is not a technical system, but rather a quality-driven framework that connects these building blocks in a professional manner.
Business Context
Starting point is Strategy, Offering and Goals.
DBRS deliberately does not start with technology or keywords, but with what, a company wants to achieve and what it stands for.
The business context defines the technical framework within which relevance arises.
Source Layer
All relevant existing contet of a company:
- Websites
- Documents
- Internal Systems (e.g. Odoo, SharePoint)
- External Sources and References
DBRS works exclusively with existing knowledge.
Nothing is invented, but rather systematically developed.
Bootstrapper & Crawler
This component collects content, standardizes formats, and assigns clear versions to them.
This creates order, traceability, and up-to-date information instead of data chaos.
AI Enrichment Layer
Content is structured, summarized, and classified semantically.
The goal is not creativity, but comprehensibility and consistency –
for humans as well as for machines and AI systems.
Index & Frontmatter Generator
The processed content is converted into clearly structured, machine-readable formats, e.g.:
- Markdown
- HTML
- JSON-LD
This creates referenceable entry points that can be reliably used by search engines and AI systems.
DBRS LLM Knowledge Hub
The central Reference System of DBRS.
An authoritative, versioned knowledge and context hub used by various systems, e.g.:
- Samy
- Interne Search
- AI-supported Applications
- External Platforms
The Knowledge Hub provides context and authority without interpreting content itself.
Relevance Evaluation
During this phase, checks are done whether the content is factually correct, commercially viable, and relevant in the context of the defined objectives.
Relevance is not simply asserted, but systematically examined and documented.
The following are used, among others:
- Canonical Context Analysis (CCA)Checks whether content is consistent and used correctly in the defined technical context.
- Canonical Context Registry (CCR)Serves as a referenced inventory of valid terms, meanings, and contexts, creating a common semantic basis. Example: Setting dieser Webseite.
- Relevance Radar with Relevance MappingShows how well content statements - e.g., from SEO or marketing contexts - are substantiated and quotable in the DBRS in terms of technical and contextual accuracy.
- The result is a comprehensible, documented, and assessable relevance that serves as a basis for further use.
Delivery Layer
The results are made available where they are needed:
- for people (website, PDFs, management)
- for search engines
- for AI systems and LLMs
The delivery layer ensures consistent use of the same knowledge across all channels.
Downstream Systems / Consumers
Downstream systems such as Samy, intranet searches, or partner platforms access the Knowledge Hub.
without altering its authority or content.
DBRS remains the referencing authority.
How effective solutions are created with open innovation engineering and mentoring
The tasks described are efficiently supported by AI-powered tools and professionally managed, designed, and monitored by the project team. DBRS provides a clear frame of reference so that decisions can be made in a context-aware, transparent, and targeted manner.
This allows DBRS implementations to be carried out in a focused manner and system migrations to be prepared in a targeted way.
Start with a Quick-Check
Alignment of strategy, goals, reality, and framework conditions.
The quick check clarifies early on what really needs to be solved - and what doesn't
Experience Innovation as a common framework
Solutions arise from the real-life experiences of management, employees, and customers.
Acceptance is not a downstream “change issue,” but part of development.
Context Engineering
Relevant information, rules, terms, and decision-making logic are deliberately clarified and documented.
This way, people, systems, and AI share the same technical context.
Digital Engineering
Configuration and interaction of the systems:
Software, interfaces, AI, workflows, and existing IT systems are set up appropriately.
Targeted, integrated, and not oversized.
Iterative implementation in manageable steps
Early results instead of lengthy concepts.
Learning, refining, and prioritizing are integral parts of the process.
Relevance and impact Assessment
Ongoing comparison: Does the solution fulfill its intended purpose?
If not, adjustments will be made – objectively, transparently, and comprehensibly.
System Handover with Clarity
The solution is handed over in such a way that it can be understood, operated, and further developed internally.
No hidden dependencies, no black box.
Training based on real-world use
No tool demos, but practical empowerment in the work context.
Those involved know why they are doing something—not just how.
Management mentoring during and after implementation
Support with decisions, priorities, and responsibility.
Mentoring ensures that the solution has an impact in everyday life.
Sustainable Anchoring in the Company
Processes, knowledge, and systems remain compatible and independent –
even without permanent external support.
DBRS is platform- and system-independent
The Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS) is not tied to a specific operating system or manufacturer.
It works equally well in Windows, Linux, or macOS environments—on the intranet, in the cloud, or in a hybrid setup.
DBRS does not focus on specific platform features, but rather on:
- structured content,
- explicit context,
- clear validity and responsibilities,
- as well as comprehensible relevance and authority rules.
This keeps DBRS stable even when operational systems change—for example, in the case of:
- Replacement of an old SharePoint system,
- Introduction of SharePoint Server Subscription Edition or SharePoint Online,
- Use of Teams, Copilot, or other AI assistants,
- Change of IT platform (Windows ↔ macOS ↔ Linux).
Important:
DBRS is not just another collaboration or planning system.
It is a cross-system reference and context instance that determines which information is considered reliable in which context—regardless of where it is technically stored or processed.
- Systems can change.
- Context and meaning must not.
Practical Tips
Relevance = visible content AND context AND intelligent processing by humans and AI
Relevance = visible content ∧ context ∧ intelligent processing by humans and AI
- Expertise, data, experience, and documents—available both internally and externally.
- ContextClassification according to objective, situation, role, timing, and question.
- Intelligent processing By humans and AI: understandable, traceable, verifiable, and effective.
If one of these components is missing, there is no relevance:
- Content without context remains meaningless.
- Context without content remains empty.
- Intelligent processing without both leads to incorrect or random results.
DBRS focuses precisely on this logical AND connection.
AI projects are effective and attract particular attention
The Digital Business Relevance Suite (DBRS) enhances the AI visibility of companies, not in terms of reach, but in terms of quotability, contextual clarity, and technical relevance—both externally and within the company. Quotable SEO claims strengthen their weight.
- Wir empfehlen bewusst kleinere und abgegrenzte Projekte, damit die Beteiligten KI-Innovation sicher und positiv erleben können.
- Die Projektmethode Experience Innovation (weiter unten beschrieben) sorgt dafür, dass KI, Menschen und Prozesse verlässlich und erfolgreich zusammenwirken.
Harvard Business Review Studie: Überwindung der organisatorischen Hindernisse für die Einführung von KI (engl.).
Better use of AI in structured and documented creative and engineering modes
Many people use AI portals in unstructured creative mode: they try things out but document little. This means that the practical benefits remain unclear and learning is random—a recent Harvard study refers to an “invisible wall” preventing further benefits.
Vibe Mode (structured creative mode)
Structured experimentation: testing ideas, trying out learning content, recognizing patterns, building initial solutions and prototypes.
The end result is understandable, comprehensible, and verifiable results, ideally a simple prototype with a brief description—the basis for the next step.
CAISE Mode (Engineering-Mode)
This is where the quality-oriented, documented development process begins with a clear goal.
AI acts as a supportive team member, decisions and results are validated:
That's what we call Collaborative AI Supported Engineering (CAISE).
Example of DBRS implementation in accordance with current technical LLM specifications
An example of how the technical DBRS page is integrated into a website can be found at https://tolksdorf.digital/dbrs-llm-knowledge-hub/ . The page is purely an informational landing page that has been deliberately kept simple to facilitate the work of LLM/AI.
Questions and Answeres - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What exactly is artificial intelligence and how do you deal with it?
How does an LLM “think”?
A large language model (LLM) does not think. It calculates the most likely answer based on data, context, and statistics. Very useful—but not infallible.
Why is artificial intelligence (AI) actually intelligent?
An LLM, also known as AI, is excellent at handling language and therefore appears intelligent, even empathetic, to users.
How do people think?
Human thinking is embodied, emotional, social, and culturally influenced. We combine experience, perception, and emotion—far more than mere information processing.
Strength lies in connection:
People contribute experience, goal orientation, and judgment—LLMs provide speed, structure, and ideas.
Together, they form a powerful duo: human-led, AI-supported, and significantly better than either side alone.
How do large language models (LLM) and artificial intelligence (AI) affect SMEs?
The answer to this question varies depending on one's disposition. It is an astonishingly feasible innovation step that can bring enormous benefits to companies of all sizes, or it can be detrimental. It should not be ignored.
Does AI bring greater efficiency or effectiveness, or perhaps nothing at all?
- As with any tool, its everyday use determines how useful it is. A tool is useless if it just sits in a box.
- Greater effectiveness: Initially, the gains in skills and opportunities outweigh the losses.
- Greater efficiency: Once new skills have been acquired, learned, and tested, the efficiency gains outweigh the costs in recurring applications.
What challenges may arise during implementation?
- Administrator access to the website must be possible; alternatively, close cooperation with those responsible is necessary.
- Data quality and distribution in data silos: Our suite helps to prepare and utilize this data.
- Acceptance within the team: AI tools such as Samy are new – we offer training courses to help employees feel confident using the technology.
- If search engine optimization (SEO) has not yet been carried out on the website, this topic is added. AI is used to reduce the amount of work involved.
Why is there no fixed price, and what costs can be expected?
- Every company has its own starting point, which leads to different workflows and levels of effort.
- Context Engineering: Data processing. AI is used to reduce effort, and results are checked by humans.
- Prompt engineering for AI used in workflows.
- Workflow and integration engineering for planned workflows.
- There are templates for the workflows, but customization and testing are still required.
- Experience value for the effort: a few hours to a few days per workflow.
What benefits can be expected?
- This is determined in the Relevance Radar Workshop and the Quick Checks.
- ChatGPT & Co find them and formulate answers that suit you instead of guessing or ignoring them.
- Truly intelligent interactive chatbots improve customer loyalty and surprise users in a positive way.
- Improvement of data quality for further processes.
- Increasing digital maturity and innovative strength.
Can the Digital Business Relevance Suite be used elsewhere?
- Yes, for internal processes.
Can I continue to use my existing website?
- Yes, the Digital Business Relevance Suite complements your website. Code snippets invisible to users are added and robots.txt and sitemap.xml are supplemented.
What do SEO and GEO mean?
- SEO = Search Engine Optimization, i.e. optimization for traditional search engines
- GEO = Generative Engine Optimization, i.e., optimization for AI such as Google Gemini, ChatGPT, Claude, Mistral, and many more.
- SEO and GEO are equally important these days
- Further information can be found at https://tolksdorf.digital/kmu-opensource-ki-hub
How secure are the data and AI itself?
- Security is not only about where the AI is operated (“hosted”) but also how it is integrated. In this solution, all user inputs in the chat client are anonymized, which allows for a wide range of AI options on this side. In each case, it must be checked whether European solutions such as the open source LLM Mistral are preferable for compliance reasons.
- Sustainable security also includes the freedom to choose between different LLM providers. This allows future or changed requirements to be taken into account.
Wie verbessert man die Sichtbarkeit bei Suchmaschinen wie z.B. Google und BING sowie KI wie Perplexity, Gemini, chatGPT?
DBRS ermöglicht die Orchestrierung der Webseiten Informationen gemäss AI Overviews (Google Search), Helpful Content / E-E-A-T, ehemals Search Generative Experience (SGE).
Die Optimierung für Suchmaschinen und KI-Systeme (oft als GEO – Generative Engine Optimization bezeichnet) erfordert eine Kombination aus klassischen SEO-Methoden und neuen, dialogorientierten Strategien.
- Kombinierte Optimierung:Die Sichtbarkeit wird durch die Kombination klassischer SEO-Methoden mit dialogorientierten GEO-Strategien verbessert.
- Answer-First-Prinzip:Zentrale Antworten werden direkt zu Beginn eines Absatzes oder Artikels platziert, da KI-Systeme gezielt nach kompakten Antworten suchen.
- Strukturierte Daten:Inhalte werden mit Schema.org-Markups (JSON-LD) ausgezeichnet, um Suchmaschinen und KI-Systemen eine eindeutige Interpretation zu ermöglichen.
- Frage-Antwort-Formate (FAQs):Inhalte werden in klaren Frage-Antwort-Strukturen aufgebaut, wobei W-Fragen als Überschriften genutzt werden, da diese häufig von KIs extrahiert werden.
- Autorität und Vertrauen (E-E-A-T):Die Glaubwürdigkeit wird durch Autorenprofile, Quellenangaben, Studienverlinkungen und Erwähnungen auf etablierten Drittplattformen gestärkt.
- Konversationelle Inhalte:Texte werden in natürlicher, dialognaher Sprache verfasst, da KI-gestützte Suchsysteme solche Inhalte bevorzugt zitieren.
- Technische Zugänglichkeit:Der Zugriff für KI-Crawler wird ermöglicht (z. B. über robots.txt), und relevante Inhalte werden direkt im HTML bereitgestellt.
- Aktualität und Faktenbasis:Inhalte werden regelmäßig aktualisiert, da aktuelle Daten und Statistiken von KI-Systemen bevorzugt berücksichtigt werden.
Fachliche Leitung / Subject Matter Lead: Rainer Tolksdorf | Tolksdorf.digital